Plane Estimation
Two Step Estimation
Plane estimation is a fairly common problem for point-cloud related applications. I Below is an example 3-face-object and the corresponding estimated planes. The algorithm is a two step process: first apply RANSAC to fit a plane (green) and obtain inlier, then use linear regression to optimize the result with inliers. Note that a L2 cost is selected since measurement of points are often subject to gaussian noise in real world.
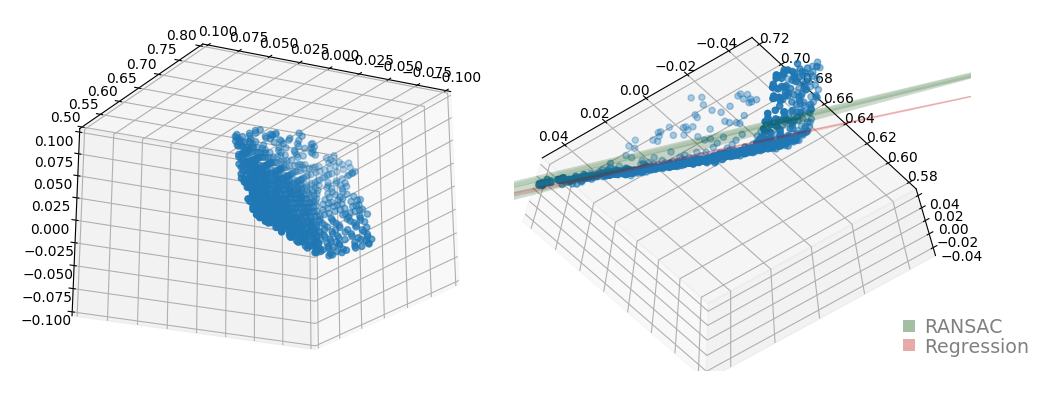
RANSAC and Linear Regression
In the previous post about RANSAC, we already learnt that RANSAC is susceptible to surrounding points. Since the model is only concern about the number of inliers, instead of their quality i.e. distance to plane, the estimation could easily be off. On the other hand, linear regression takes into account the quality of each point, and therefore generates a plane that fits more closely to input points. However, linear regression could be slow and trap in local minima, therefore RANSAC offers a good initialization.
Remarks
- Although having the same mathematical form (gradient descent), Deep learning is about learning an unknown mapping from the input space to the output space. Meanwhile, optimization has a clear idea about its underlying mapping e.g. homogeneous transformation matrix, the whole purpose is about selecting the optimal one from the candidate space.
- It should be easy for deep learning e.g. shellnet to detect multiple planes at once. But it would hard for it to identify a specific plane. Probably it’s more reasonable to assign them with semantic meanings, pick meaningful ones, then do plane fitting.